190.WHAT IS THE BRAIN?
Of all the things that distinguish man from the rest of the animal kingdom, the most important is his brain. Many of the lower animals have no brain at all, or a tiny one, or one that is poorly developed. For instance, an earthworm has a brain about the size of a pinhead, a rabbit has a thimble-sized brain. The brain of a man weighs, on the average, about 1.3 kilograms.
By the way, the size of the brain is not the most important thing about it. An elephant has a bigger brain than man, but it is not as well developed.
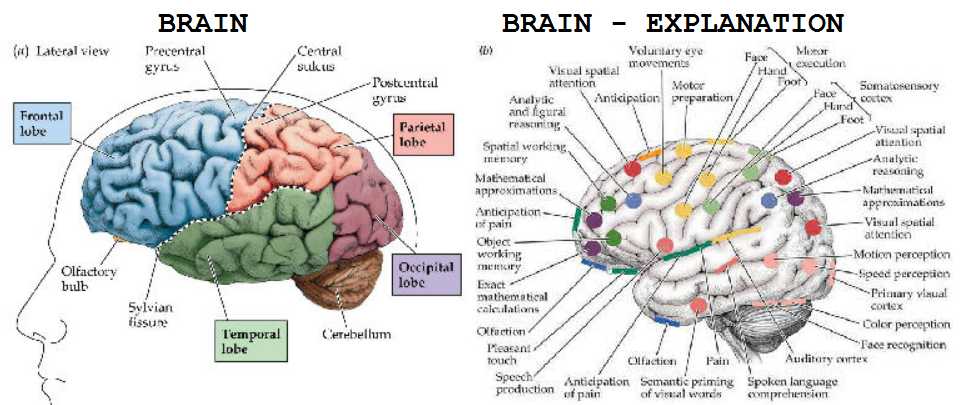
The brain has three main divisions: the cerebrum, the cerebellum, and the medulla oblongata. The cerebrum is considered the most important part. It is from here that all our voluntary actions are controlled.
The cerebrum is also the biggest part of man’s brain, filling most of the space in the upper and back part of the skull. The cerebrum is divided into two equal parts or hemispheres, and its surface is covered with wrinkles and folds. This surface is composed of gray matter, made up of cells. The higher the type of animal, the more numerous and deeper are the folds. Under this surface, called the cortex, there is white matter which is made up of nerve fibers. Through this part pass the messages to and from the cortex.
Certain sections of the cortex control certain body functions, so every part of the cortex is different. Science can point to certain parts as the controls over sight, or feeling, or hearing, or movement of certain muscles. That’s why an injury to just one part of the brain (for instance, by a blood clot) can impair one’s capacity to perform a certain function, such as speech.
The cerebellum is in the back of the skull, beneath the cerebrum. It controls the power of balancing and the co-ordination of the muscles. If it is injured, a man may not be able to walk in a straight line or stand erect.
The medulla oblongata is about the size of the end of the thumb and is found at the end of the spinal cord. It controls breathing, the beating of the heart, digestion, and many other activities that seem to go on by themselves. This is where the nerve fibers that go from the brain to the spinal cord cross. One side of the brain controls the other side of the body. The right half of the cerebrum, for example, controls the left leg, and so on.


Leave a Reply