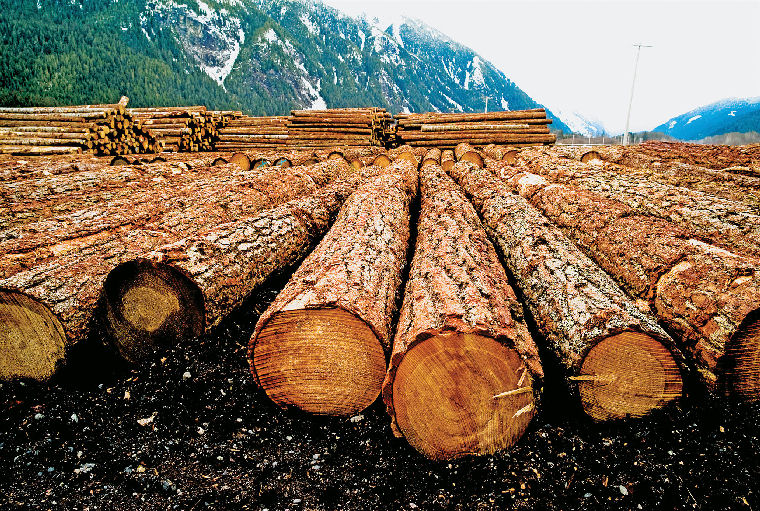
73.HOW DOES A TREE BECOME LUMBER?
Lumbering was one of the earliest industries to be started in America. In fact, there is a legend that Leif Ericson, who was supposed to have visited North America about the year 1000, brought back a cargo of timber from the new world! We do know that one of the first products shipped to England from the Jamestown colony was timber from the Virginia forests.
There are many trees used for building and other purposes. The leading softwood trees include pine, Douglas fir, hemlock, spruce, white fir, cypress, and redwood. Hardwood timber or lumber used for furniture making, flooring, and certain other special purposes comes from such trees as oak, gum, maple, poplar, and walnut.
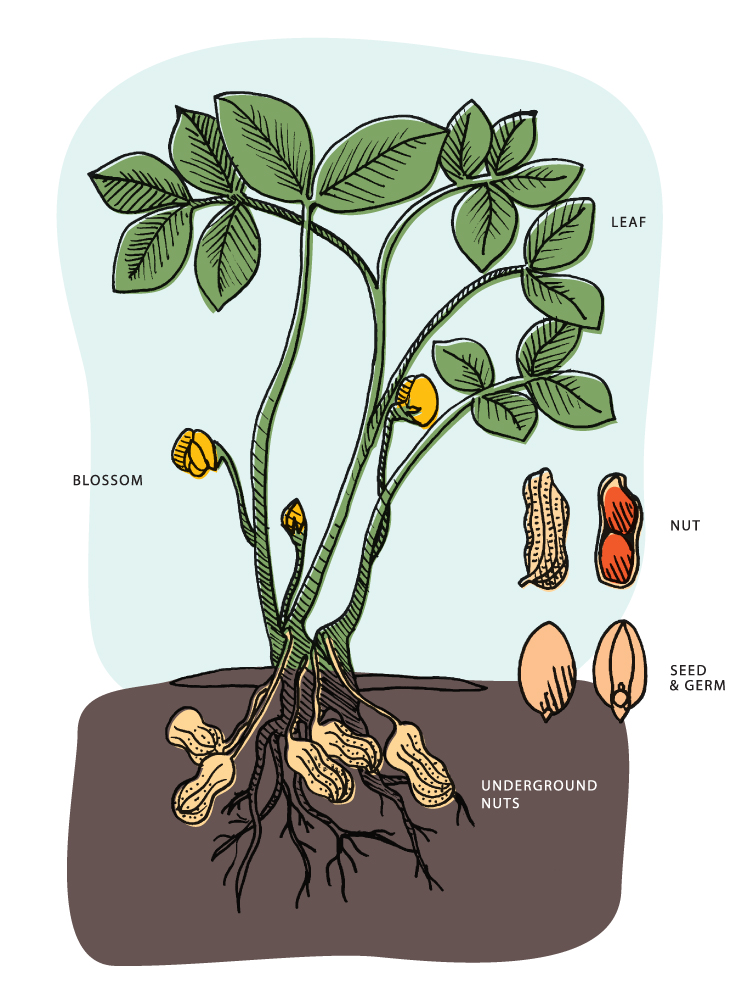
72.HOW DO PEANUTS GROW?
When you look at the unopened pod of the peanut, you can see that it closely resembles the pea or bean. In fact, it belongs to the same family. The peanut plant is a bush, and its blossoms resemble those of the pea.
After the petals fade, a part of the pod elongates very greatly and its tip becomes buried in the soil. There this tip enlarges and the seeds mature. So if you want to gather peanuts, you have to dig them out of the soil!
71.WHAT GROWS IN THE ARCTIC REGION?
There is a difference between the Arctic Region and the Arctic Circle. The Arctic Circle goes around the northern part of the earth in a perfect circle, 66.5 degrees north of the equator. At one time, the Arctic Region was considered to be all land and water lying north of this circle.
But today, the Arctic Region is considered to be a geographical unit based on the combination of a number of different elements, especially vegetation and climate. It extends south into Canada and includes all of Greenland.